A product teardown is a systematic dissection of a product to analyze its features, design decisions, user experience, and overall strategy. The goal isn’t just to understand what a product does, but how it does it and why it was built in that way.
Product teardowns provide valuable insights into a product’s functionality, design, and market positioning, making them an indispensable tool for you as a product manager.
Unlike simple product reviews, teardowns are deeply technical and analytical. They uncover the mechanics behind a product’s design and provide actionable insights to refine your product strategy, benchmark against competitors, and identify gaps in the market. Keep reading to learn more about them, including the tools you can use to conduct them and real-world examples.
What is a product teardown?
A product teardown offers a window into the competitive landscape. It provides a foundation for understanding why competitors made specific decisions, how those decisions impact their users, and what opportunities might exist for your product. Teardowns also serve as a strategic exercise, allowing you to:
- Benchmark your product against industry leaders
- Identify areas of differentiation and innovation
- Refine your product roadmap based on real-world insights
In short, product teardowns can be the difference between a product that struggles to gain traction and one that leads its category.
Why conduct product teardowns?
Product teams often operate in competitive and fast-evolving environments where understanding user needs and market dynamics is critical. Without a structured way to analyze competitors, you risk making decisions based on assumptions rather than data. Teardowns solve this problem by:
- Providing actionable insights into how competitors solve user problems
- Highlighting opportunities for improvement or innovation in your product
- Equipping you with a framework for structured competitive analysis, ensuring no critical details are missed
The product teardown process
To conduct a meaningful product teardown, follow these steps:
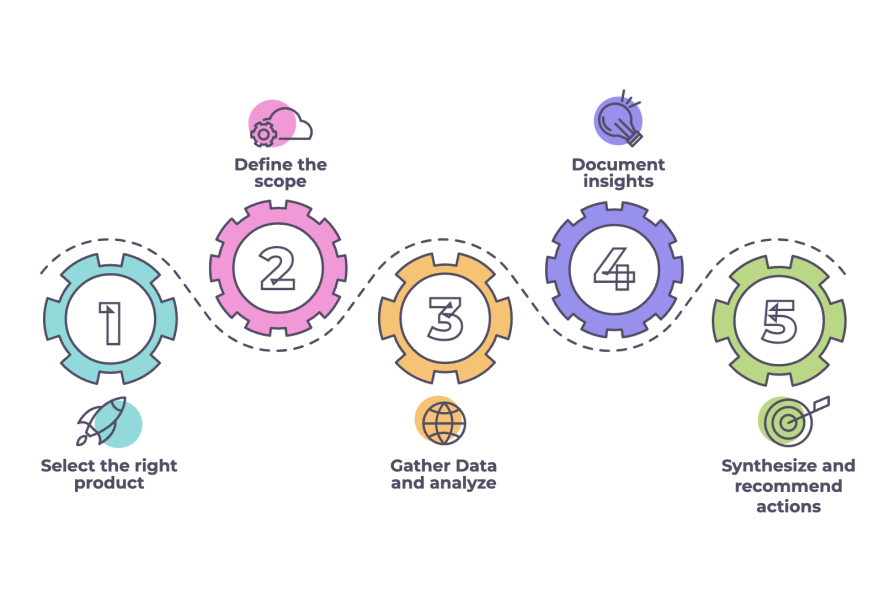
1. Select the right product
Choosing the right product is the first and most critical step:
- Direct competitors — Start with products that solve the same problem for the same audience. For example, if you’re building a team collaboration tool, products like Slack and Microsoft Teams are obvious choices
- Adjacent products — Sometimes, inspiration comes from outside your direct category. For instance, a teardown of Duolingo’s gamification strategies might reveal opportunities for a task management app to improve user engagement
2. Define the scope
A product is a complex system, so it’s essential to focus on specific elements:
- Feature-level — Examine one or more core features, such as search functionality or user onboarding
- Workflow-level — Analyze end-to-end user journeys, like account setup or checkout processes
- Design-level — Focus on UI and UX choices, accessibility, and visual hierarchy
3. Gather data and analyze
A comprehensive teardown involves multiple layers of analysis:
- Functionality — What does the product do? What are its standout features?
- Usability — How easy is it for users to achieve their goals? Are there friction points?
- Technical implementation — What technologies power the product? How scalable is its architecture?
- Business alignment — How do the product’s design and features align with its business goals, such as revenue generation or user acquisition?
4. Document insights
Organize your findings in a way that’s easy to share with your team. Use tools like:
- Miro or Notion for collaborative documentation
- Figma for UI analysis
5. Synthesize and recommend actions
Finally, turn your teardown findings into actionable recommendations. For example, if you discover that a competitor’s onboarding process significantly reduces churn, propose specific enhancements to your onboarding flow.
Tools for conducting product teardowns
Teardowns can be resource-intensive, but the right tools can streamline the process:
- UI analysis tools
- Inspect element — For web products, browser developer tools are invaluable for deconstructing layouts, CSS properties, and DOM structure
- Figma — Helps recreate user interfaces for documentation and analysis
- User behavior / analytics tools
- LogRocket — Captures session replays, heatmaps, and user interaction flows, providing in-depth insights into how users navigate and interact with your product. Its ability to track frontend performance and connect user behavior with underlying issues makes it ideal for pinpointing and resolving UX challenges
- Collaboration and documentation tools
Case studies: Detailed examples of product teardowns
To help better illustrate a product teardown, pay attention to the following examples from three successful organizations.
Slack
Slack helps make work happen by providing work management and productivity tools.
Onboarding:
Slack’s onboarding flow sets the standard for turning new users into engaged teams:
- Guided setup — First-time users are led through a series of steps to set up a workspace, create channels, and invite teammates. This ensures they immediately see Slack’s value
- Gamification — Slack employs micro-celebrations, like confetti animations, to make onboarding feel rewarding
Core features:
Slack excels in creating an ecosystem of productivity:
- Channel-based communication — Solves the problem of email clutter by allowing focused discussions in channels
- Third-party integrations — With integrations for tools like Google Drive, Zoom, and Trello, Slack becomes indispensable for cross-functional teams
Design:
- Minimalist aesthetic — Slack’s clean UI ensures users can quickly navigate even complex workflows
- Accessibility options — Features like dark mode and adjustable notification settings cater to a wide range of user preferences
Business model:
Slack’s freemium model balances user acquisition and monetization:
- Free tier — Attracts small teams with core functionality
- Paid plans — Offer features like unlimited search history and enterprise-grade security, encouraging businesses to scale within the platform
Netflix
Netflix is a leading example of a digital product that has mastered personalization and user retention.
User onboarding:
- Personalized recommendations early — Netflix immediately asks users about their preferences during onboarding, using this data to populate a curated homepage. This minimizes decision fatigue and ensures users see content that resonates with their tastes
- Account creation process — Netflix allows a seamless transition from free trials to paid plans, with a focus on reducing churn through subscription reminders and easy cancellation policies
Core features:
- Recommendation algorithm — Netflix’s machine learning-based recommendation engine analyzes viewing history, time of day, user preferences, and regional trends to surface highly personalized suggestions. This algorithm is so effective that over 80 percent of views come from recommendations
- Offline viewing — Recognizing the needs of users in areas with poor internet connectivity, Netflix offers offline downloads for its app users, a feature that directly addresses market-specific challenges
Design and UX:
- Seamless navigation — The interface is consistent across devices, ensuring users can pick up where they left off on any platform
- Content previews — Hovering over a movie or show automatically plays a preview, helping users decide what to watch without additional clicks
- Profiles — The ability to create multiple user profiles under a single account makes Netflix family-friendly and ensures individual personalization
Business model:
Netflix’s subscription-based model encourages recurring revenue. The tiered pricing strategy offers options for different budgets while highlighting premium features like Ultra HD streaming.
Shopify
Shopify is a go-to platform for entrepreneurs looking to build and manage e-commerce stores. Its success lies in simplifying a complex process while offering scalability.
Onboarding:
- Streamlined setup — Shopify makes it easy for new users to get started by guiding them through domain setup, theme selection, and payment processing integration
- Education during onboarding — Shopify provides bite-sized tutorials and FAQs during the onboarding process, empowering users with just-in-time knowledge to overcome common hurdles
Core features:
- App ecosystem — Shopify’s marketplace offers thousands of third-party apps, allowing merchants to customize their stores with features like email marketing, inventory management, and SEO tools. This modular approach ensures Shopify meets the needs of both small businesses and large enterprises
- Payment integration — Shopify payments eliminates the need for third-party payment processors, providing a frictionless checkout experience. Additionally, it supports multiple currencies to facilitate international sales
- Mobile Optimization — All Shopify themes are mobile-first, ensuring an excellent shopping experience for end users
Design and UX:
- Customization without coding — Shopify’s drag-and-drop editor makes it easy for merchants to design professional-looking storefronts without technical skills
- Analytics dashboards — Shopify provides detailed analytics, from traffic sources to conversion rates, enabling merchants to make data-driven decisions
Business model and strategy:
Shopify offers tiered pricing to cater to businesses of all sizes. Its revenue model also includes transaction fees and revenue-sharing agreements for apps in its marketplace, ensuring consistent monetization.
Lessons from the case studies
Each of these examples highlights different aspects of what makes a product successful:
- Slack excels in communication and ecosystem stickiness
- Netflix leverages personalization to retain users
- Shopify prioritizes usability and extensibility to empower its customers
By conducting a teardown of these or similar products, you can draw actionable insights that directly influence your product’s strategy, ensuring it remains competitive and user-centric.
Using insights from teardowns to improve your product
Here’s how you can leverage teardown findings effectively:
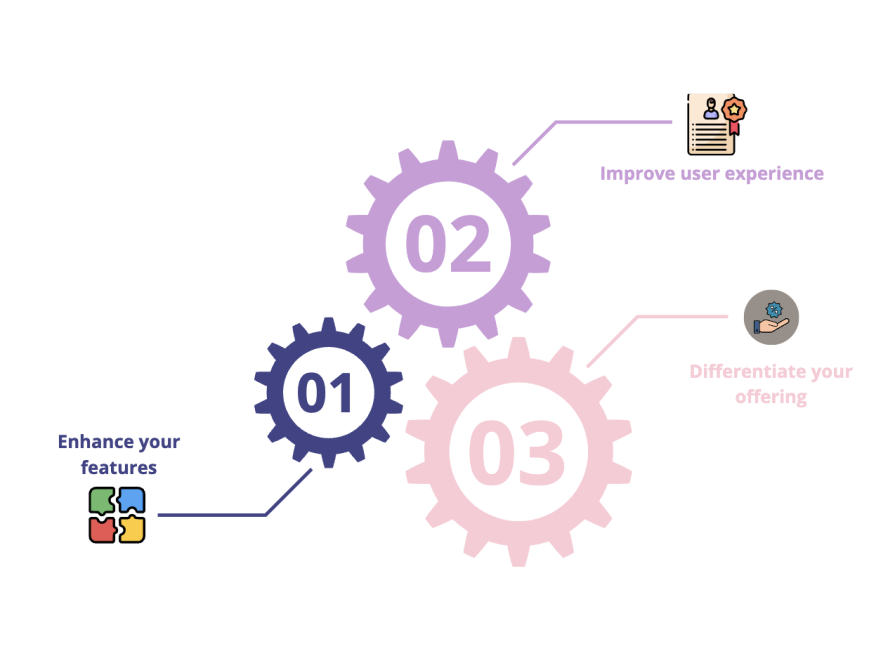
Enhance your features
If a teardown reveals that a competitor offers a more robust implementation of a feature, use it as a benchmark. For instance, if a teardown of Zoom highlights its advanced breakout room functionality, you might prioritize building a similar feature in your video conferencing app.
Improve your user experience
Insights from competitors can uncover ways to reduce friction. For example, if another product simplifies onboarding by pre-filling user data with single sign-on (SSO), consider implementing a similar feature.
Differentiate your offering
Teardowns help identify gaps in competitors’ products that you can exploit. If most task management apps neglect accessibility, positioning your app as inclusive could carve out a niche.
Final thoughts
Product teardowns are powerful tools for PMs, providing a data-driven approach to competitive analysis and product strategy. They allow you to:
- Benchmark against industry leaders
- Identify opportunities for innovation
- Refine your product roadmap with actionable insights
To maximize the value of teardowns, make them a recurring part of your product management process. Start with focused analyses, document insights, and use them to drive meaningful changes.
Over time, you’ll find that product teardowns aren’t just about understanding competitors, they’re about continuously improving your product to better serve your users.
Featured image source: IconScout
The post What is a product teardown? Process, tools, and other insights appeared first on LogRocket Blog.